
5 Diseases Caused by Bacteria on Tilapia, Red Tilapia
| Mon, 03 May 2021 - 10:14
Tilapia (tilapia) has many causes, but in the framework of this article, we focus on presenting 5 common diseases occurring in tilapia related to bacteria.
MAS (Motile Aeromonas Septicaemia) syndrome
MAS syndrome caused by Aeromonas hydrophila and related species. This is a heterotrophic, rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium mainly found in warm climates. Aeromonas hydrophila is also known as "cannibal bacteria".
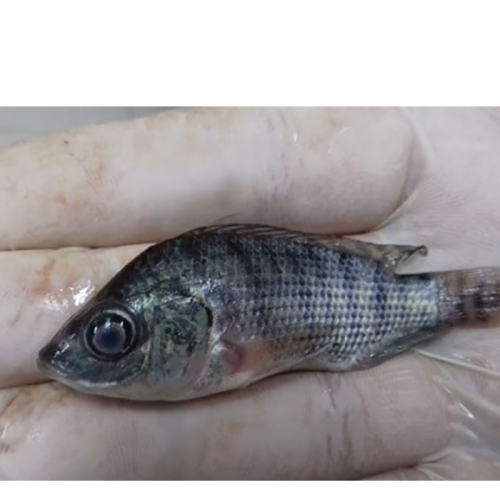
Infected fish show an imbalanced swimming pattern; lethargic swimming; breathing on the surface of the water; hemorrhagic or inflamed skin and fins; goggle; opaque cornea; a swollen abdomen with cloudy or bloody liquid; low daily mortality.

Tilapia infected manifested abdominal swelling, hemorrhage.
Treatment: Disinfect pond with KMnO 4 at 2-4 mg / liter or bath diseased fish in 4-10 mg / liter for 1 hour; antibiotics can be used for treatment, but professional consultation is required.
Also read: New Strains, New Gains For Nile Tilapia Producers
Vibriosis
Vibrio anguillarum and other species. Gram-negative bacteria with curved rods. Vibrio is a common bacterium and is causing serious harm to the aquaculture and fishing industries.
Fibrillation has symptoms similar to MAS syndrome; The disease has been reported with environmental fluctuations such as poor water quality or herd stress.
Treatment: According to published studies, the best solution to treat tremor in tilapia is to use antibiotics in food. However, we strongly recommend that, consult an expert on the use of antibiotics for the best effect.
Columnaris Disease
The disease is caused by the bacteria Flavobacterium columnare , a Gram-negative rod-like bacteria of the genus Flavobacterium . This name is derived from the way in which this type develops in the "rhizome" column formation. This bacterium is also considered to be an important pathogen in tilapia farming.
Fish infected with the bacteria exhibit frayed fins and / or irregular white to gray patches on the skin and / or fins; lesions, pale color, necrosis on gills.
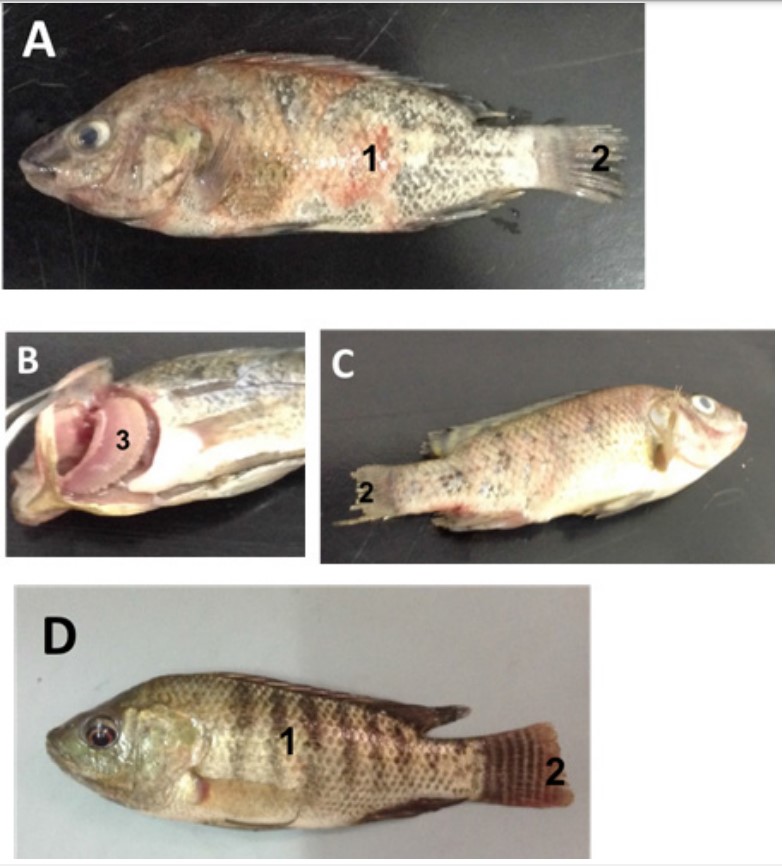

A) Infected fish have an ulcerated and hemorrhagic outer surface (1) and an eroded tail fin (2). B) Infected fish show pale gills (3). C) Infected fish have hardened body and eroded tail fins (2). D) Normal tilapia
Treatment: It is possible to use antiseptic by KMnO 4 as with MAS syndrome; or use CuSO 4 at 0.5-3 mg / liter, depending on the alkalinity of the pond.
Also read: Streptococcus Vaccine Offers Hope for Tilapia Sector
Edwardsiellosis
Edwardsiella tarda bacteria are the main cause of the disease. This is arbitrary, small, easy to move anaerobic, gram-negative, straight rod-shaped.
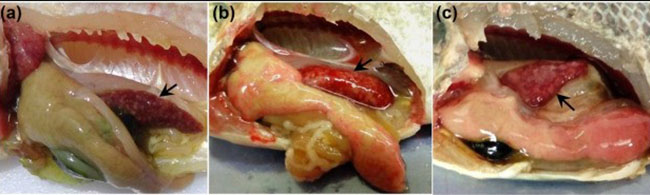
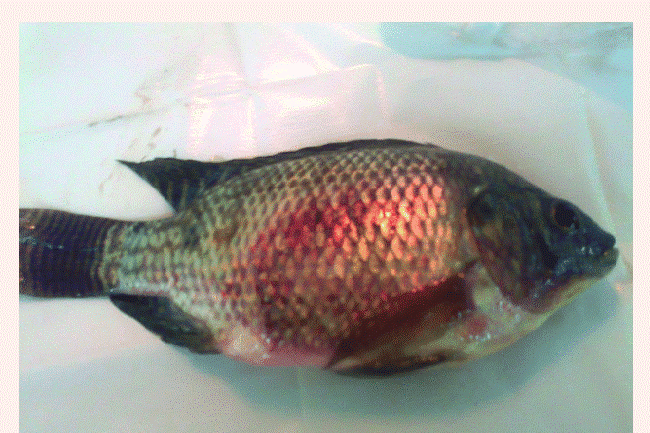
Infected tilapia have few external symptoms; bleeding, or blood fluid in the body cavity; pale, speckled liver; swelling, dark red spleen; tender, swollen kidneys.
Infected red snapper exhibits dark red spleen, swollen liver, and white spots appear
Treatment: Consider when using antibiotics in fish food when sick. It is also important to pay attention to the amount of antibiotics used and the length of time fish are stored in the pond before commercial sale.
Also read: The Bacterium that's Battling Streptococcus in Tilapia
The disease is caused by streptococci
The causative agent includes 2 main species of the disease, Streptococcus iniae and Enterococcus sp. is a Gram-positive bacteria invading and causing disease in tilapia parents and tilapia from 50 - 300g. The suitable temperature for streptococcal disease on tilapia grows from 25 - 35 0 C, which thrives most when the water temperature is above 30 0 C. Ponds with a high mortality rate of fish are umbrella ponds. Contaminated and rich in organic matter, mortality can be as high as 80% in a short time, however, when the temperature is low, the mortality rate will decrease.
Infected fish show comatose manifestations, erratic swimming; melasma, darkening of the skin; one side bulging ankle and a milky film above the eye; bloating; intestinal bleeding, around the mouth, anus, and fins; enlarged spleen, almost black; high mortality.
Treatment: Antibiotics can be used in food under consultation and supervision from a specialist. The recommended dose of Erythromycin is 50mg / kg fish / day for 12 days.
Source: Tepbac.com






















